Dental labs depend on metal alloys to deliver restorations that meet clinical demands for longevity. Metal alloys are used in this process for their strength and adaptability. They appear in crowns, bridges, and partial dentures to provide stable structures. Here’s more information about how dental labs use metal alloys in oral restorations:
Dental labs fabricate PFM crowns by casting a metal framework with porcelain layers. The alloy framework helps distribute biting forces evenly across the crown, minimizing the risk of fractures. Porcelain layers mimic the translucency of natural enamel and seamlessly blend with adjacent teeth. Technicians scan or model the prepared tooth to design the framework. The alloy is cast to precisely match the tooth’s margins and contours. Porcelain layers are carefully built up to control the shade and anatomical features of the crown. Firing cycles in a furnace bond the porcelain securely to the underlying metal.
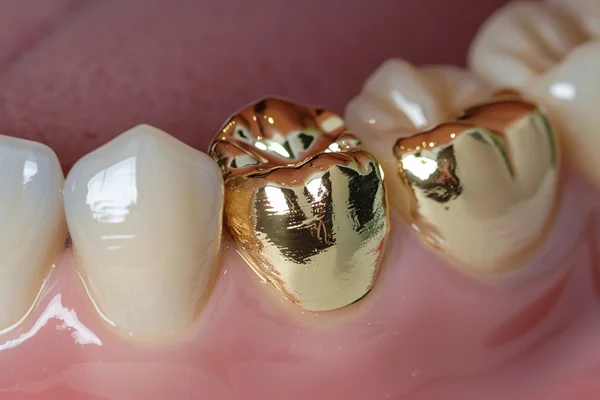
Labs choose between base-metal or noble alloys based on the functional and esthetic needs of the case. Base-metal alloys offer strength and corrosion resistance, while noble alloys improve porcelain bonding and offer long-term biocompatibility. Technicians and clinicians collaborate to select the appropriate alloy based on the functional, esthetic, and patient-specific needs.
Custom abutments connect dental implants to the final restorations, completing the prosthetic process. These components are individually designed to fit the patient’s anatomy and the specific implant system, providing optimal stability and function. A custom abutment directly supports a crown, bridge, or denture by attaching securely to the implant fixture.
Dentists collaborate with technicians to design and fabricate abutments that fit precisely and support the planned restoration. Technicians use clinical data and digital impressions to determine the ideal angulation, contour, and height, verifying the final prosthetic complements adjacent teeth. The abutment is then refined to the design specifications, with careful attention to accurate margins and fit.
The materials used for custom abutments must adapt precisely to implant platforms and withstand long-term functional stress. Titanium alloys are beneficial due to their predictable osseointegration and excellent corrosion resistance in the oral environment. In other cases, noble alloys are used to achieve precise marginal adaptation and simplify the esthetic veneering process.
Partial denture frameworks rely on cast metal alloys that integrate effectively with abutment teeth and surrounding oral structures. These frameworks form the basis for rests, clasps, and connectors, providing mechanical retention and functional stability. High-corrosion-resistance alloys maintain structural integrity under long-term exposure to the oral environment. Other alloys offer elasticity, allowing for controlled flexure that distributes occlusal forces across multiple abutments, minimizing concentrated stress on individual teeth. When combined with acrylic bases and prosthetic teeth, the metal framework acts as a rigid core that stabilizes occlusal forces and maintains prosthetic alignment over time. A well-polished alloy surface also improves patient comfort and reduces soft tissue irritation.
Dental bridges restore edentulous spaces using pontics supported by a metal alloy framework. The alloy provides strength, dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance. Properly designed frameworks distribute occlusal forces across abutments, minimizing stress concentration and maintaining tooth position. Both casting and CAD/CAM workflows allow for precise fit and adaptation at the margins. Material selection is a collaborative decision between clinician and lab, based on occlusal load, esthetic zone involvement, and patient-specific factors.
Metal alloy innovations play a key role in how dental laboratories manufacture restorations. More complex formulations increase strength, improve porcelain bonding, and provide long-term wear resistance. These advances allow laboratories to precision-engineer frameworks and tailor restorations to clinical requirements. Find a dental laboratory to review available materials and discuss how alloy selection benefits restorative treatments.